In this tutorial, we have to write a function to find first node of loop from given linked list. If the loop exists, it returns the first node in the loop. Otherwise, it returns NULL.
Example :
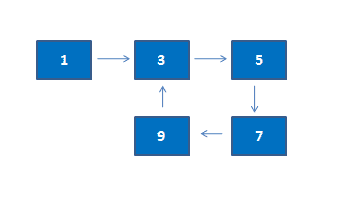
In above program, 3 is the first node of loop
Example – Program to find first node of loop in a linked list
We will use below steps to find first node of loop in a linked list.
- If a loop is found, initialize a slow pointer to head, let fast pointer be at its position.
- Move both slow and fast pointers one node at a time.
- The point at which they meet is the start of the loop.
public class LinkedListFirstLoop {
static Node head;
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d) {
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
Node detectFirstLoop(Node head) {
if (head == null || head.next == null) {
return null;
}
Node slowPtr = head;
Node fastPtr = head;
// Move slowPtr and fastPtr 1 and 2 steps
slowPtr = slowPtr.next;
fastPtr = fastPtr.next.next;
// Search for loop
while (fastPtr != null && fastPtr.next != null) {
if (slowPtr == fastPtr) {
break;
}
slowPtr = slowPtr.next;
fastPtr = fastPtr.next.next;
}
// If loop does not exist
if (slowPtr != fastPtr) {
return null;
}
// If loop exists. Start slowPtr from head and fastPtr from meeting point.
slowPtr = head;
while (slowPtr != fastPtr) {
slowPtr = slowPtr.next;
fastPtr = fastPtr.next;
}
return slowPtr;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedListFirstLoop list = new LinkedListFirstLoop();
list.head = new Node(1);
list.head.next = new Node(3);
list.head.next.next = new Node(5);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(7);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(9);
// Creating a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next;
Node firstNode = list.detectFirstLoop(head);
if (firstNode== null) {
System.out.println("No loop found");
} else {
System.out.println("First loop node is : " + firstNode.data);
}
}
}
Output:
First loop node is : 3