Write a program that checks if a given Linked list contains a loop and returns true if the loop exists. If the list does not contain a loop, false is returned. The following figure shows a linked list with a loop.
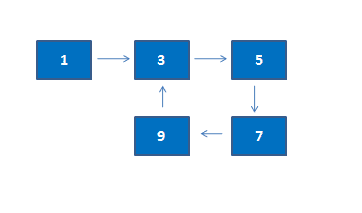
Example – Program to Detect loop in a linked list
In this program , we will use Floyd’s loop detection algorithm :
- Use the two pointers variable fastPtr and slowPtr to initialize both to head of the linked list.
- Move fastPtr to two nodes and slowPtr to one node for each iteration.
- If fastPtr and slowPtr meet at some iteration , there is a loop in the linked list.
- If fastPtr reaches the end of the link list without meeting the slowPtr, there is no loop in the linked list.
public class LinkedListLoopDetect{
private Node head;
private static class Node {
private int value;
private Node next;
Node(int value) {
this.value = value;
}
}
public void addToTheLast(Node node) {
if (head == null) {
head = node;
} else {
Node temp = head;
while (temp.next != null)
temp = temp.next;
temp.next = node;
}
}
public void printNodes() {
Node temp = head;
while (temp != null) {
System.out.format("%d ", temp.value);
temp = temp.next;
}
System.out.println();
}
public boolean ifLoopExists() {
Node fastPtr = head;
Node slowPtr = head;
while (fastPtr != null && fastPtr.next != null) {
fastPtr = fastPtr.next.next;
slowPtr = slowPtr.next;
if (slowPtr == fastPtr)
return true;
}
return false;
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
LinkedListLoopDetect list = new LinkedListLoopDetect();
Node loopNode=new Node(3);
list.addToTheLast(new Node(1));
list.addToTheLast(loopNode);
list.addToTheLast(new Node(5));
list.addToTheLast(new Node(7));
list.addToTheLast(new Node(9));
list.printNodes();
// creating a loop
list.addToTheLast(loopNode);
System.out.println("Loop existed-->" + list.ifLoopExists());
}
}
Output
1 3 5 7 9 Loop existed-->true
Example – Program to Detect and Remove loop
public class LinkedListLoop {
static Node head;
static class Node {
int data;
Node next;
Node(int d)
{
data = d;
next = null;
}
}
int detectAndRemoveLoop(Node node)
{
Node slowPtr = node, fastPtr = node;
while (slowPtr != null && fastPtr != null && fastPtr.next != null) {
slowPtr = slowPtr.next;
fastPtr = fastPtr.next.next;
if (slowPtr == fastPtr) {
removeLoop(slowPtr, node);
return 1;
}
}
return 0;
}
void removeLoop(Node loop, Node curr)
{
Node ptr1 = null, ptr2 = null;
/* Set a pointer to the beginning of the Linked List and
move it one by one to find the first node which is
part of the Linked List */
ptr1 = curr;
while (1 == 1) {
/* Now start a pointer from loop_node and check if it ever
reaches ptr2 */
ptr2 = loop;
while (ptr2.next != loop && ptr2.next != ptr1) {
ptr2 = ptr2.next;
}
/* If ptr2 reahced ptr1 then there is a loop. So break the
loop */
if (ptr2.next == ptr1) {
break;
}
/* If ptr2 did't reach ptr1 then try the next node after ptr1 */
ptr1 = ptr1.next;
}
/* After the end of loop ptr2 is the last node of the loop. So
make next of ptr2 as NULL */
ptr2.next = null;
}
void printList(Node node)
{
while (node != null) {
System.out.print(node.data + " ");
node = node.next;
}
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
LinkedListLoop list = new LinkedListLoop();
list.head = new Node(1);
list.head.next = new Node(3);
list.head.next.next = new Node(5);
list.head.next.next.next = new Node(7);
list.head.next.next.next.next = new Node(9);
// Creating a loop for testing
head.next.next.next.next.next = head.next;
list.detectAndRemoveLoop(head);
System.out.println("Linked List after removing loop : ");
list.printList(head);
}
}
Output
Linked List after removing loop : 1 3 5 7 9